what is the core function of an enterprise platform
- By Infoik
- 27 Nov, 2021

A Complete Guideline of Core Functions of Enterprise Platform
If more than ten people choose to return the same pair of ill-fitting jeans every other day for a month, their order will likely be refunded. The system must register this item and mark it before reporting casualties or assessing any situation behind closed doors. All seems well at first glance, but have you ever thought about how long these reports take? Behind each cash, register sound are complex software systems known as an enterprise that process transactions quickly without error!
What are Enterprise Software Systems?
The success of any business depends on how quickly it can collect and analyze data, which is why large corporations like Walmart use enterprise information systems. These complex platforms handle many operations within a company to facilitate its reporting tasks. They’re built for speed with scalability in mind, designed to deploy across networks such as the Internet or an intranet, and offer easy access via web browsers or mobile apps so that employees can get their jobs done no matter where they are!
However, the complexity of enterprise applications pushes most corporations to outsource the development of these programs they need for their operations; after being developed and then brought back into-house with an IT team specializing in this type of work – deployment happens.
The 3 Types of Enterprise Systems
To stay competitive in today’s digital markets, every corporation needs three types of enterprise systems.
Customer Relationship Management

CRMs are software that helps companies present a consistent message about their customer insights by gathering the latest information on each lead. Collections of data for CRM use happen at each step during pre-sales processes like sales and marketing, call centers, help desks, and support services.
CRM is a significant component of any company’s operations. It takes in customer service activity from every aspect, customer management, recording every order and exchange processed by the business while also keeping track of invoices cut for shipment sends as well as refunds given out to customers at each step along their journey with you. Not just when they buy but even if there was some kind of problem or issue following up after delivery too!
What are Examples of CRM?

There are two types of CRMs that every business process should be familiar with: operational and analytical. Operating systems focus on automating customer-facing parts, like targeted communications and offers. At the same time, analytics concentrate more heavily on analyzing data such as sales history, credit scores, or marketing loyalties for enhancements to both customers’ value and company profitability.
The most popular CRMs used by corporations include:
- Salesforce – The platform is geared towards mid-size companies and businesses not familiarized with CRM, implementing automation for lead data management in addition to customer profile information centralization; this type of enterprise system falls under general software categories.
- HubSpot – Services provided range from marketing content creation to web analytics, making them an Inbound Software company!
- Zoho CRM – This software is aligned with offering project management tools and services that companies need, like word processing, spreadsheets, and wikis;
- Freshsales CRM– Are you in the market for new sales tracking systems? If so, this cloud platform offers industry-specific features such as contact management or lead tracking!
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
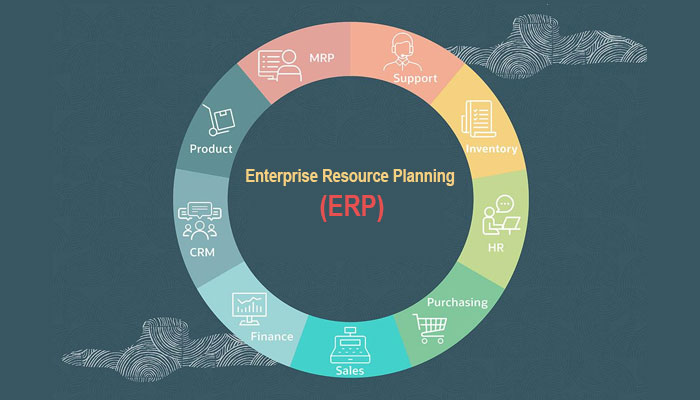
ERP systems are designed to unify the process of an enterprise, making it easier for companies and employees within that organization. The software integrates all aspects under one roof. So, there’s no more inconsistent actions or duplicate work across different departments; instead, you can use what has already been tested by other businesses in your field!
What is Enterprise Resource Planning Used For?
To help your organization reach its goals, make sure to look at what kind of ERP modules align with the different areas in which you specialize. For example:
- Manufacturing: The manufacturing module of an ERP system is used to manage engineering, scheduling capacity, access control, and quality control. It also includes product life management functions like workflow or production line monitoring for efficient operations across all departments within your business enterprise, with the goal being to increase productivity while reducing costs along the way!
- Accounting/Finance: By streamlining cash management tasks and other accounting functions, ERP systems can offer businesses real-time data performance while ensuring compliance with financial regulations. This system is easily controlled by finance teams.
- Human Resources: The HR department of a company can use the ERP system to track data on training, recruiting, and payroll, among other things. The information gathered by this module helps them manage benefits for their employees and measure KPIs such as how many people were hired or promoted within specific time frames.
For some companies, cloud-based ERP is the way to go. Its cost efficiency and flexibility will create a seamless experience for employees while maximizing productivity in your company’s operations! Moreover, in this modern age, cloud model, cloud services, cloud versions, cloud transformation, and cloud computing are widely used around the world.
“A 2018 study by Allied Market Research predicts that global market value of cloud-based enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems topped $32 million that year increasing at an annualized rate 6% over 2017.”
Supply Chain Management Systems
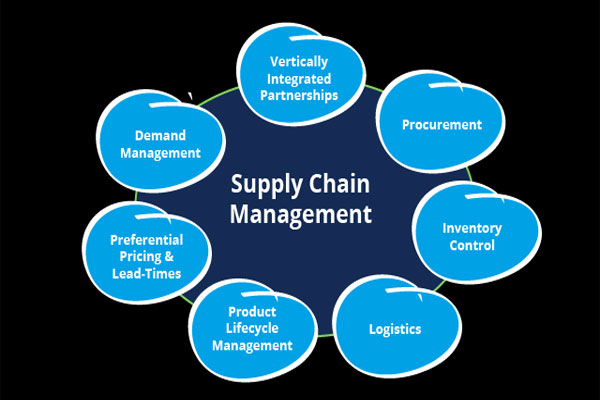
The third type of enterprise application is supply chain management systems. These software programs monitor the relationships between people, tasks, or equipment to facilitate integrated partnerships amongst all goods and services points across an entire company’s business network. From suppliers on one end who produce products for sale as well as clients on another.
Supply chain management is the process of ensuring that goods are delivered to their destination in an efficient manner. There are many different types, but some common ones include purchasing, inventory management, and warehousing. Among others for retail companies or production industries with extensive inventories like manufacturers who produce semi-finished products which another company can then finish before being sold on.
Major Enterprise IT Landscape/ Applications
The enterprise system umbrella can include specific applications with a more detailed level of architectural design and reliability. They’re mostly built for handling precise data, going through rigorous testing to assure accuracy in information. An example is the following:
1. Email Marketing Systems: Email marketing is a great way to promote new products and services regularly. Companies often use web analytics in order analyze data from their campaign, showing how many page views were gained by the messages being sent out onto customers’ inboxes every day or week depending on what best suits your needs as well as those of companies who have paid for advertising space within emails directed at yours specifically.
2. Business Intelligence: Business intelligence is an umbrella term that includes tools and practices to access any information, analyze it efficiently for organizations to optimize work performance.
3. Payment Processing: Third-party services that process payments are now faster and more diverse due to more robust wireless internet connections. Services like PayPal offer clients more payment options, which makes enterprises systems adaptable for scaling financial data.
The changing business landscape of today’s world means that firms must be able to adapt for them not only to survive but thrive. Enterprise resource planning systems are becoming more innovative and efficient with each passing day, providing companies with crucial information about their competition, so that they can stay ahead at all times.
Whether it is staying on top competitor-wise or gaining an edge over other local competitors by understanding what others might do beforehand which will enable you to get your product/service into someone else’s market first.
What is the Core Function of an Enterprise Platform
Every successful business needs a platform to function. Every single one has four core functions for business:
- Matchmaking
- Building liquidity
- setting rules & standards for others, and
- Providing functionality itself with its transactions on the market
The first step in creating your ecosystem of buyers is by doing these four key things right!
Matchmaking
There are many different people with varying interests and needs. Each group has its motivations, which drive them to interact in ways that can be monetized through business models like advertising or subscription services. Understanding this will help you maximize your potential for success by understanding how users’ personas impact what they value most about the product/service being offered on an individual level.
For example, Uber matches drivers nearby based solely on their location along with whether there is someone requesting pick up at any given moment.
Building Liquidity
The chicken and egg problem is a common challenge that every platform needs to solve as it grows. However, there are seven strategies you can use for your business’s success in overcoming this issue, with one process involving value subsidies on both sides of an ecosystem user-side engagement!
The use of value subsidies can be used to promote your company, product, or service. For example, a referral fee for signing up with one’s friend on Uber and free rides when referring other drivers is an example of monetary value subsidies while offering better rates through the VIP program may provide product support in exchange for high-volume consumption like booking restaurants online before they open their doors.
Setting Rules & Standards
Platform businesses use technology to curate access and usage between multiple user groups to facilitate an exchange of value. The platform should think like the mayor for this town who can create rules that will help govern, hopefully, incentivize growth in desired directions (such as limiting messages or providing incentives). Still, most importantly, they need good information about what is happening within their community at all times!
Example: Twitter limited tweets length back when it launched – 140 characters was chosen because users found them sufficient enough; people could make brevity count through creativity while retaining crucial details without too much extra padding.
Providing Functionality
A company’s business model is a significant determinant of its value potential. To unlock that value, they have to build technology and find the right balance between features in their products and what kind of tech we develop for them.
Example: Airbnb may be the answer for those looking to make extra money on their vacation. Whether you are an avid traveler or this is your first time, Airbnb provides software that helps product managers/ producers manage booking availability and communications while calculating tax obligations from income generated by hosting guests through their website interface. In addition, they offer insurance coverage in case anything happens during a visit, such as lost property or damage was done at home.
Final Words
We all know the importance of having a platform for your business to function. But, what is an enterprise platform? Simply put, it’s a set of tools and services that help businesses grow by providing matchmaking opportunities as well as creating liquidity on their own. So now you have four key things to think about when building your ecosystem -matchmaking, building liquidity, setting rules and standards for others, and providing functionality itself with its transactions on the market. The first step in this process is making sure these functions are done right!













